Previous Post:
This time, following the installation, we will cover the basic configuration steps.
Step 1: Configure Send Connector (Must)
While receiving emails is possible without additional configuration, sending emails requires the Send Connector to be set up.
Mail flow -> send connectors -> New (+)

Specify the Connector Name -> Select Type: Internet -> Click Next.

Next

Add

Specify the FQDN (*)-> Save

Next

Click Add -> Specify the Source Server -> Click Finish.

Verify that the Send Connector has been successfully created.

Access https://localhost/owa, log in, and send a test email.
(As of the date written, emails can be sent to Outlook.com without registering an SPF record.) -> Verify the receipt of the email.

Step 2: Configure Virtual Directories (Recommended)
To enable connections from various clients like Outlook, proceed with configuring the virtual directories.
Run the Exchange Management Shell.

#Enter the URL to be used commonly across the virtual directories.
$url = "https://mail.wingtiptoys.kr"
$autodiscover = "https://autodiscover.wingtiptoys.kr"
#Set the Virtual Directory internal and external URLs to be identical.
#ECP
Get-EcpVirtualDirectory | Set-EcpVirtualDirectory -InternalUrl "$url/ecp" -ExternalUrl "$url/ecp"
#EWS
Get-WebservicesVirtualDirectory | Set-WebservicesVirtualDirectory -InternalUrl "$url/ews/Exchange.asmx" -ExternalUrl "$url/ews/Exchange.asmx"
#MAPI
Get-MapiVirtualDirectory | Set-MapiVirtualDirectory -InternalUrl "$url/mapi" -ExternalUrl "$url/mapi"
#EAS
Get-ActiveSyncVirtualDirectory | Set-ActiveSyncVirtualDirectory -InternalUrl "$url/Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync" -ExternalUrl "$url/Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync"
#OAB
Get-OabVirtualDirectory | Set-OabVirtualDirectory -InternalUrl "$url/oab" -ExternalUrl "$url/oab"
#OWA
Get-OwaVirtualDirectory | Set-OwaVirtualDirectory -InternalUrl "$url/owa" -ExternalUrl "$url/owa"
#Autodiscover
Get-ClientAccessService | Set-ClientAccessService -AutodiscoverServiceInternalUri "$autodiscover/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml"
#Run the following commands on each server.
IISReset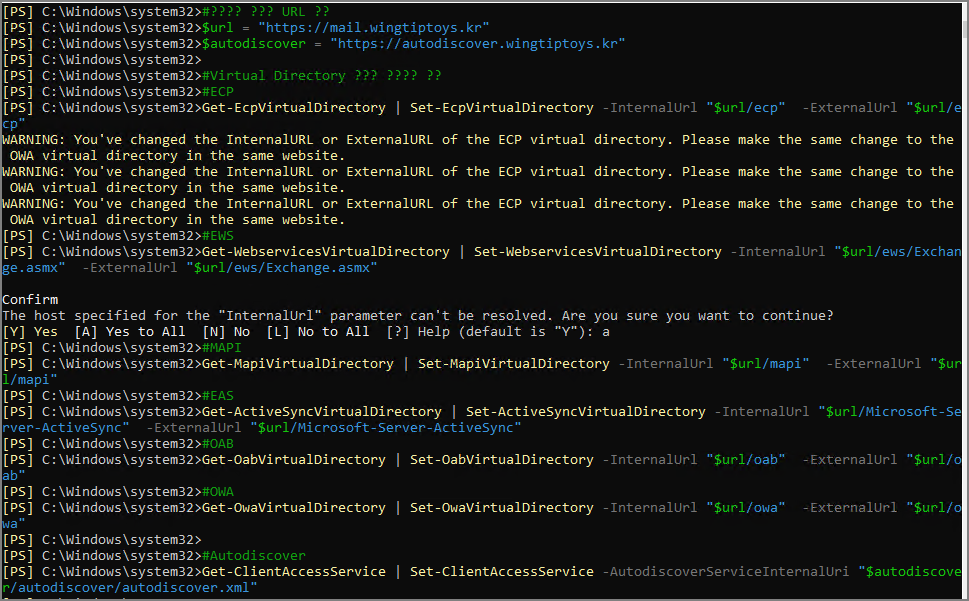
Step 3. Accepted Domain
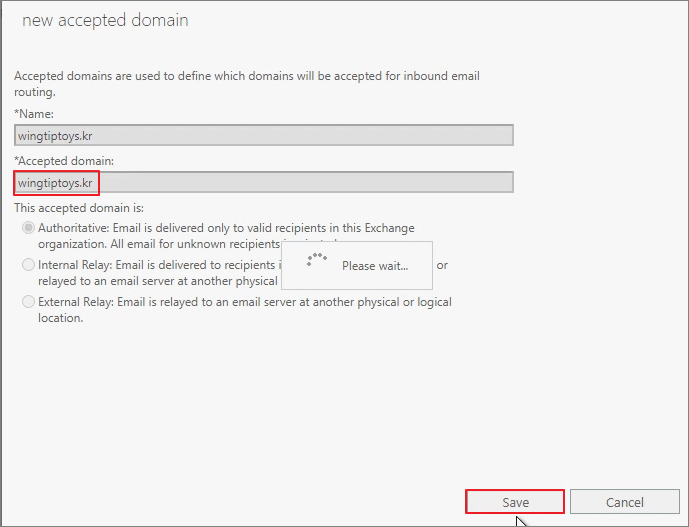
If you create a domain like Corp. or .local in a test environment, you must add an accepted domain for the actual receiving address.
Go to Mail flow -> Accepted domains -> Click + (Add).
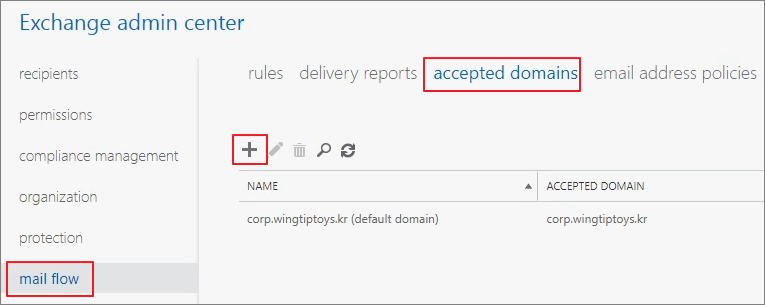
Add the domain.
Step 4. Modify Email Address Policies
To ensure that newly created mailboxes are automatically assigned to the added domain, you need to modify the Email Address Policies.
Mail flow -> email address policies -> Default Policy

Go to Email address format -> Make the necessary modifications.

Modify the Email Address Parameters.
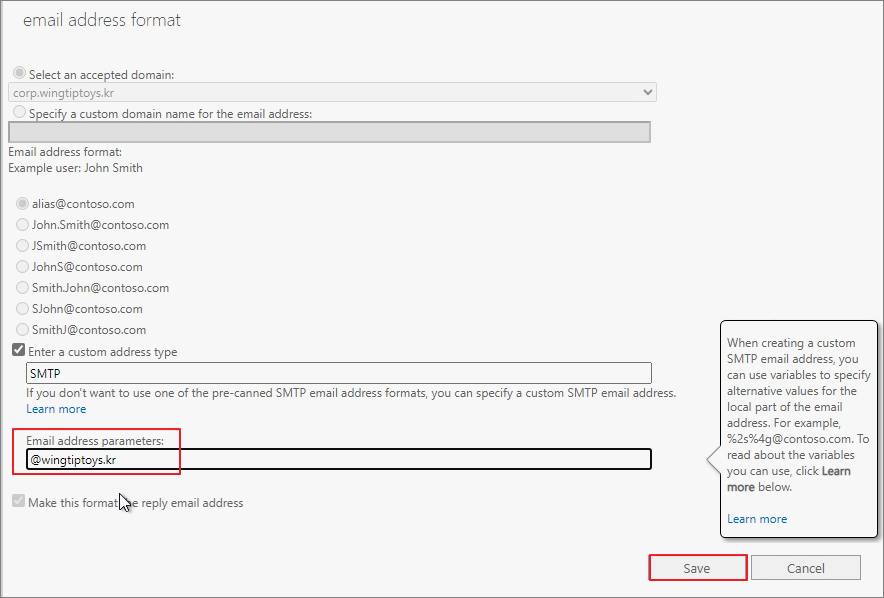
Save

Step 5: DNS Configuration (Must)
Add the values for Autodiscover, OWA, SPF, and MX records to both the internal and external DNS servers. (Refer to the video for detailed instructions.)
Example: Internal DNS

Example: External DNS

Step 6: Install Certificates (Must)
Initially, certificate requests were created through the Exchange Server UI, but recently, I’ve been using the Tool provided by Digicert for its simplicity.
In practice, most of the process is typically handled by the certificate provider.
Create CSR

I purchased a Multi SAN (Subject Alternative Name) certificate and have written this guide based on that.

Copy the CSR
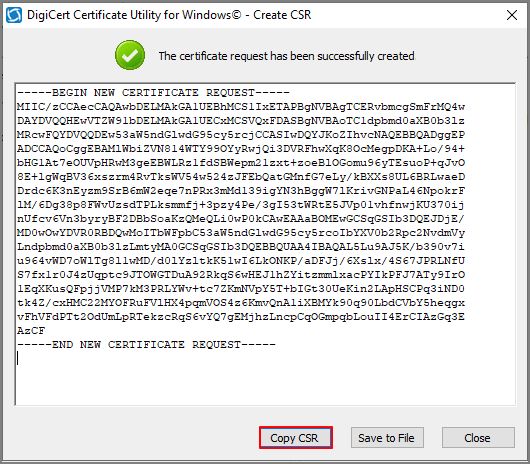
Proceed with the issuance process on the certificate provider’s website where you purchased the certificate.

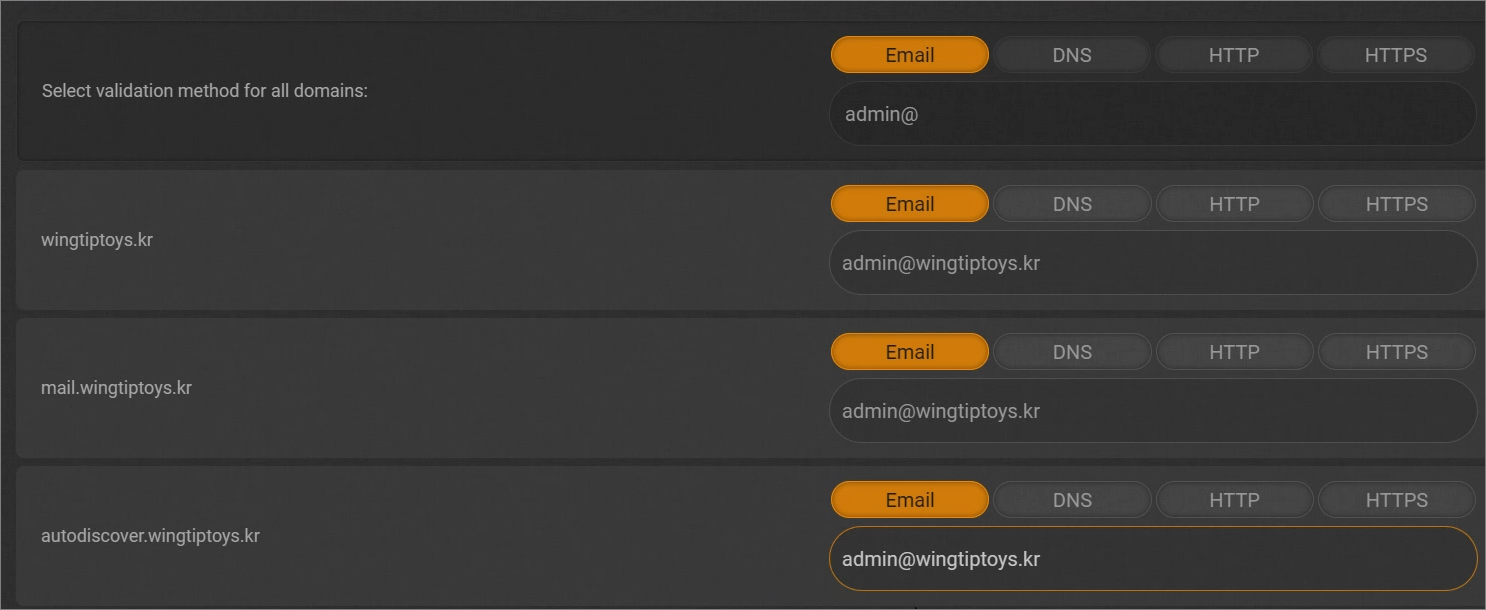
For domain verification, you can either proceed with the DNS verification process or:

Verify the domain by receiving an email and completing the authentication process.
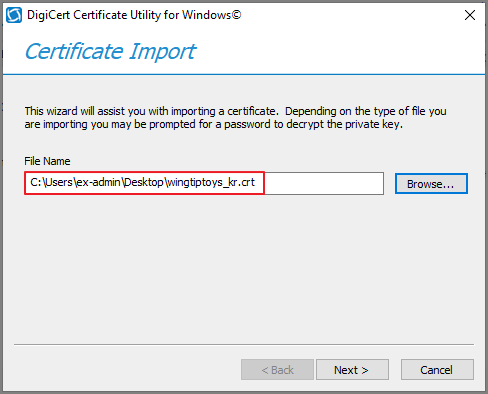
Import the issued certificate into the server.

Specify the certificate file.
Specify a name -> Click Finish.

Verify that the certificate has been successfully installed.

#View the installed certificate.
Get-ExchangeCertificate
#Certificate Binding
Enable-ExchangeCertificate -Thumbprint <Thumbprint> -Services IIS,SMTP -DoNotRequireSsl
#Restart the IIS service (requires running Exchange Management Shell with administrative privileges).
IISReset
Verify that the certificate has been correctly applied by accessing the Exchange Server from both internal and external networks.

Step 7. Manage Database (Optional)
In a company environment, it is uncommon to keep the database location and the installation path the same. Let's move it to the D drive.
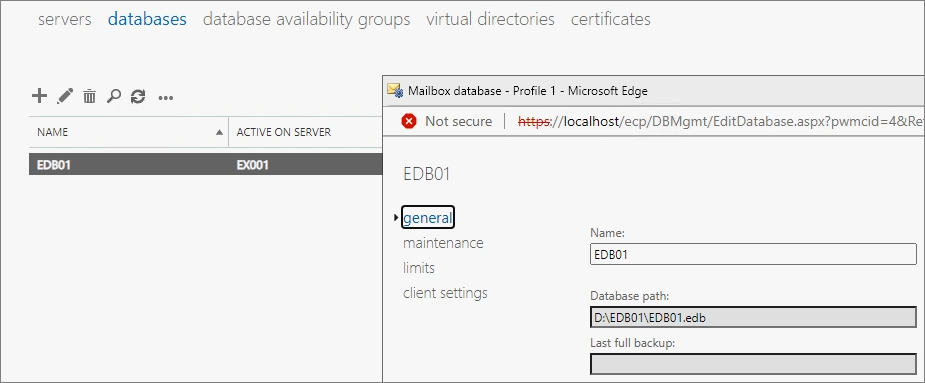
First, navigate to Servers -> Databases to check the default database name.

Perform this process on each server.
#Change Database Name
Get-MailboxDatabase -Identity "old DB name"|Set-Mailboxdatabase -Name "New DB name"
#Change the database path
Move-DatabasePath "New DB name" -EdbFilePath "D:\EDB01\EDB01.edb" -LogFolderPath "D:\EDB01\"
You can verify that the .edb and log files have been moved to the specified path.

Check the updated information in the Admin Center.
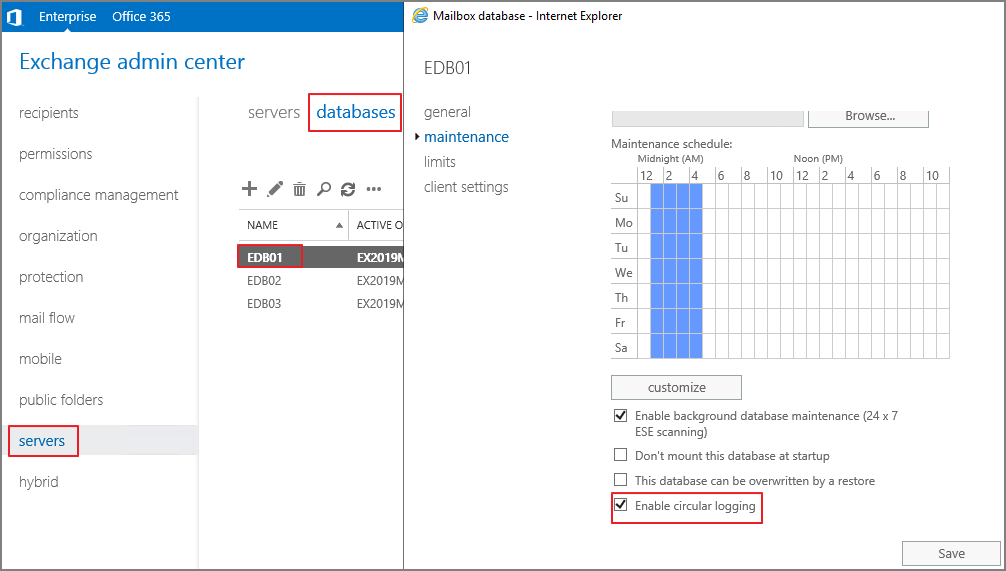
Since the log files of the database can grow significantly, it is recommended to enable circular logging if you are not using a backup solution.
Servers -> databases -> maintenance -> Enable circular logging
Step 8. Enable and change the path for mail flow logging (Optional).
Only certain areas of logs related to SMTP are enabled by default.
For Mail Flow analysis, it is recommended to activate the relevant logs and manage their paths separately.
(Since most logs will be enabled, you can disable them if they take up too much space or are deemed unnecessary.)
Change it using the following command:
#Change the location of Exchange Mail Flow Logs.
$path= "D:\ExchangeLogs"
#Frontend Transport Service
Get-FrontendTransportService | Set-FrontendTransportService -ConnectivityLogPath "$path\Frontend\Connectivity" -ReceiveProtocolLogPath "$path\Frontend\ProtocolLog\SmtpReceive" -SendProtocolLogPath "$path\Frontend\ProtocolLog\SmtpSend" -AgentLogPath "$path\Frontend\AgentLog" -DnsLogPath "$path\Frontend\DNSLog" -DnsLogEnabled $true
Get-FrontendTransportService | Set-FrontendTransportService -IntraOrgConnectorProtocolLoggingLevel Verbose
#Transport Service
Get-Transportservice | Set-TransportService -ConnectivityLogPath "$path\Hub\Connectivity" -MessageTrackingLogPath "$path\MessageTracking" -IrmLogPath "$path\IRMLogs" -ActiveUserStatisticsLogPath "$path\Hub\ActiveUsersStats" -ServerStatisticsLogPath "$path\Hub\ServerStats" -ReceiveProtocolLogPath "$path\Hub\ProtocolLog\SmtpReceive" -SendProtocolLogPath "$path\Hub\ProtocolLog\SmtpSend" -QueueLogPath "$path\Hub\QueueViewer" -WlmLogPath "$path\Hub\WLM" -PipelineTracingPath "$path\Hub\PipelineTracing" -AgentLogPath "$path\Hub\AgentLog" -DNSLogEnabled $true -DnsLogPath "$path\Hub\DNSLog"
Get-TransportService | Set-TransportService -IntraOrgConnectorProtocolLoggingLevel Verbose
#Mailbox Transport Service
Get-MailboxTransportService | Set-MailboxTransportService -ConnectivityLogPath "$path\Mailbox\Connectivity" -ReceiveProtocolLogPath "$path\Mailbox\ProtocolLog\SmtpReceive" -SendProtocolLogPath "$path\Mailbox\ProtocolLog\SmtpSend" -MailboxDeliveryThrottlingLogPath "$path\Mailbox\ProtocolLog\Delivery" -MailboxDeliveryAgentLogPath "$path\Mailbox\AgentLog\Delivery" -MailboxSubmissionAgentLogPath "$path\Mailbox\AgentLog\Submission"
Get-MailboxTransportService | Set-MailboxTransportService -MailboxDeliveryConnectorProtocolLoggingLevel Verbose
#Enable Logging about Send & ReceiveConnector
Get-SendConnector | Set-SendConnector -Protocollog Verbose
Get-ReceiveConnector | Set-ReceiveConnector -Protocollog Verbose
Verify the results.

Step 9. Disable unused Receive Connectors.
If POP3, IMAP, and Outbound Proxy are not being used, disable the connectors listed below.

Step 10. Change IIS Log Path (Optional).
One of the most resource-intensive areas in Exchange is IIS.
If not managed separately, IIS Logs can consume significant space on the C drive, so it is recommended to manage them in a separate path.
IIS Manager - [Server] - Logging

Make the following changes and apply them.

IISReset을 진행한 뒤, 아래와 같이 로그가 저장되는 것을 확인합니다.
Step 11. Configure http to https redirection (Optional)
In most corporate environments, an HTTP (port 80) request is configured to redirect to HTTPS (port 443).
The method for this is detailed in Microsoft’s technical documentation, and the following guide is based on that resource.
Configure http to https redirection for Outlook on the web in Exchange Server | Microsoft Learn
Use IIS Manager to remove the Require SSL setting from the Default Web Site.
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:access -sslFlags:None -commit:APPHOST
Use IIS Manager to restore the Require SSL setting for other virtual directories under the Default Web Site.
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/api" -section:Access -sslFlags:Ssl,Ssl128 -commit:APPHOST
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/aspnet_client" -section:Access -sslFlags:Ssl,Ssl128 -commit:APPHOST
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/Autodiscover" -section:Access -sslFlags:Ssl,Ssl128 -commit:APPHOST
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/ecp" -section:Access -sslFlags:Ssl,Ssl128 -commit:APPHOST
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/EWS" -section:Access -sslFlags:Ssl,Ssl128 -commit:APPHOST
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/mapi" -section:Access -sslFlags:Ssl,Ssl128 -commit:APPHOST
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/OAB" -section:Access -sslFlags:Ssl,Ssl128 -commit:APPHOST
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/owa" -section:Access -sslFlags:Ssl,Ssl128 -commit:APPHOST
Use IIS Manager to configure the Default Web Site to redirect to the /owa virtual directory. (Enter the actual URL you configured in this command)
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:httpredirect -enabled:true -destination:"https://mail.wingtiptoys.kr/owa" -childOnly:true
Remove HTTP redirection for the sub-virtual directories.
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/API" -section:httpredirect -enabled:false -destination:"" -childOnly:false
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/aspnet_client" -section:httpredirect -enabled:false -destination:"" -childOnly:false
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/ecp" -section:httpredirect -enabled:false -destination:"" -childOnly:false
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/ews" -section:httpredirect -enabled:false -destination:"" -childOnly:false
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/mapi" -section:httpredirect -enabled:false -destination:"" -childOnly:false
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/owa" -section:httpredirect -enabled:false -destination:"" -childOnly:false
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/powershell" -section:httpredirect -enabled:false -destination:"" -childOnly:false
%windir%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/rpc" -section:httpredirect -enabled:false -destination:"" -childOnly:false
Restart IIS
IISRESET

If there are multiple production servers, repeat the same process on all servers.
How to Verify Functionality:
- On a client computer, open a web browser and enter the URL:
http://<ServerName> - Verify that the request is redirected to Outlook on the Web (HTTPS) and confirm that you can log in.
- Open the following URL in the browser:
http://<ServerName>/owa - Check again that the request is redirected to Outlook on the Web (HTTPS) and ensure you can log in successfully.
Make sure the port 80 forwarding is set to point to the Exchange server.
When you input the following command and press Enter,

It will be redirected as shown below.

Step 12. Change Queue Database Location (Optional)
Change the location of the queue database | Microsoft Learn
Typically, the Queue Database (Queue DB) is located in the following path:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\TransportRoles\data\Queue

When emails accumulate in the queue, the Mail.que file increases in size. If it reaches a level where disk space becomes insufficient, the Transport Service will stop. To prevent such service disruptions in advance, the location of the Queue DB is often changed and managed.
Create a new folder for the Queue DB. (In the test environment, it was set to the D drive, but in a production environment, it is recommended to use a location separate from the database.)

Run the Command Prompt as an administrator.
Execute the following command:
Notepad %ExchangeInstallPath%Bin\EdgeTransport.exe.config

Locate the following path:
<add key="QueueDatabasePath" value="<LocalPath>" />
<add key="QueueDatabaseLoggingPath" value="<LocalPath>" />

Make the following changes -> Save:
<add key="QueueDatabasePath" value="D:\Queue" />
<add key="QueueDatabaseLoggingPath" value="D:\Queue" />

Restart the Microsoft Exchange Transport Service.

You can verify the changes as shown below.

Step 13. Specify the Offline Address Book (OAB) (Optional)
Assign the Offline Address Book (OAB) to each database.

This concludes this post. When delving into details, each item has its own prerequisites. If the opportunity arises, I will cover each topic in greater detail.